What is BIOS?
A BIOS stands for “Basic Input Output System”, is a chip on the motherboard. It is stored in the computers and it is a ROM (Read Only Memory) chip and EPROM (Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) is also known as firmware. It will support all hardware on a 286 AT PC and drivers are required for all other hardware. The original version is 8088 BIOS.
 |
| BIOS |
Functions of BIOS
It stores a set of instructions to tell the PC how to control devices and provides low-level hardware access. It tests hardware on startup using POST and runs “bootstrap loader” after POST. After this, the operating system takes over.
The BIOS sit between the hardware and the operating system
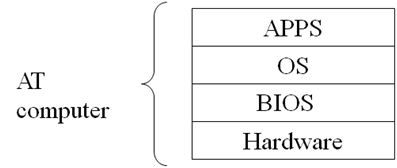 |
| BIOS Location |
Four Stage Model of Computing
Model of Computing
Startup Routine
- POST
- Bootstrap Loader
- Master Boot Record
- IO.SYS
- NTLDR
1. During the POST, the BIOS tells drivers to “test themselves” and report back. The problems are flagged either by beeps codes or by messages on the screen.
e.g. 301- Keyboard failure
2. Bootstrap Loader
3. Master Boot Record
After this the operating system takes over.
POST
It only checks devices listed in Basic Input Output System. “Devices go forth and test yourselves”.
- Beep Codes
- Text Errors
- Missing NTDLR
- Keyboard error or no keyboard present
- POST cards POST Error Codes
Error Code - Device
100 Series Error (any error in the range 100-199) - Motherboard
200 Series Error (any error in the range 200-299) - RAM
300 Series Error (any error in the range 300-399) - Keyboard
400 Series Error (any error in the range 400-499) - Monochrome Video
500 Series Error (any error in the range 500-599) - Colour Video
600 Series Error (any error in the range 600-699) - Floppy Drive
1700 Series Error (any error in the range 1700-1799) - Hard Drive
Boot Process
- CPU’s power good wire “wakes up” the CPU
- CPU reads first line of POST program
- Bootstrap loader runs
- Check if disk is in FDD drive
- Look for O.S. on boot sector of hard drive N
- TLDR or IO.SYS is loaded into RAM
- Control is transferred from bootstrap loader to the O.S.
- Core O.S. files, drivers and services are loaded into RAM
BIOS Types
The following Basic Input Output System types are
- Motherboard chipsets
- Each BIOS designed for a specific chipset
- 2Mb of storage
- 8088 PC – 384K
- Backward compatability
- BIOS Manufacturers
- AMI
- Award
- Phoenix
Updating the BIOS
- Original BIOS chips couldn’t be updated that is EEPROM or Flash ROM.
- Updates downloaded from Internet
Why update?
- Support for new hardware
- Overcome a BIOS bug
- “Flashing” the BIOS
Device Drivers - It is installation disk which loaded into ram on startup.
Config.sys - Config.sys told the OS where the device drivers were stored. It was located on your hard drive and it is used with the windows operating system and it was originally used with DOS. It is also known as SYSEDIT.
System.ini - It allowed backward compatibility for older device drivers. It was originally use with windows operating system.
Registry - In windows, config.sys and system.ini were consolidated in the registry. The registry holds all the configuration settings. It can be accessed through the control panel or device manager and you can also manage directly through regedit and regedit32.

Comments
Post a Comment